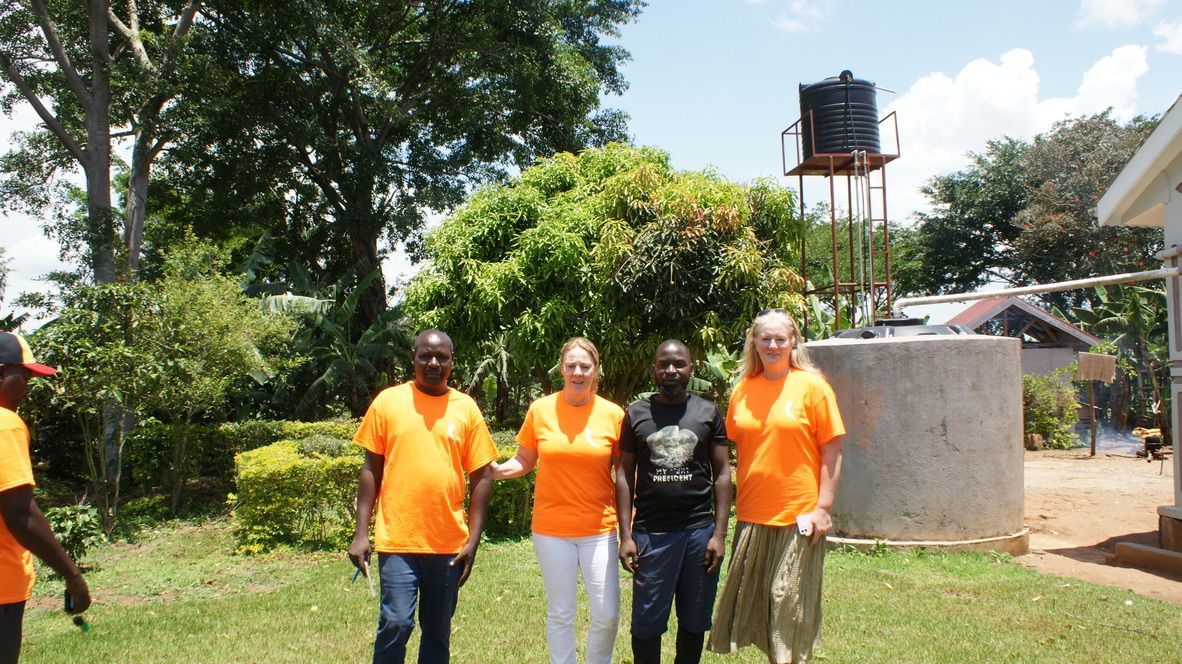
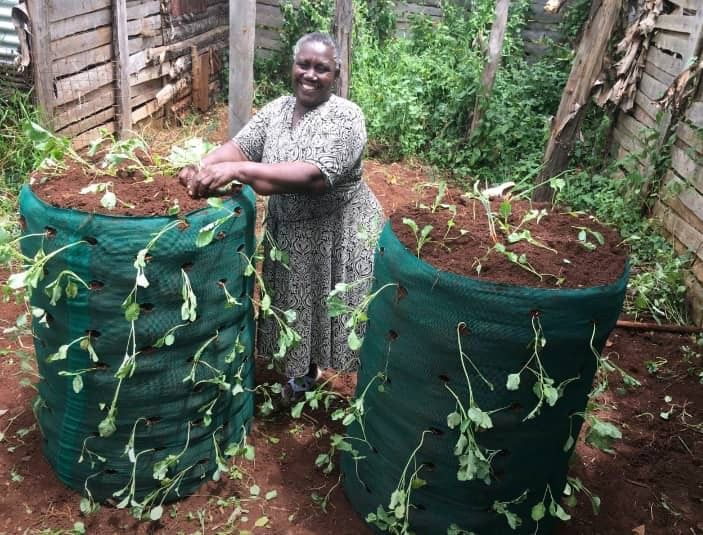
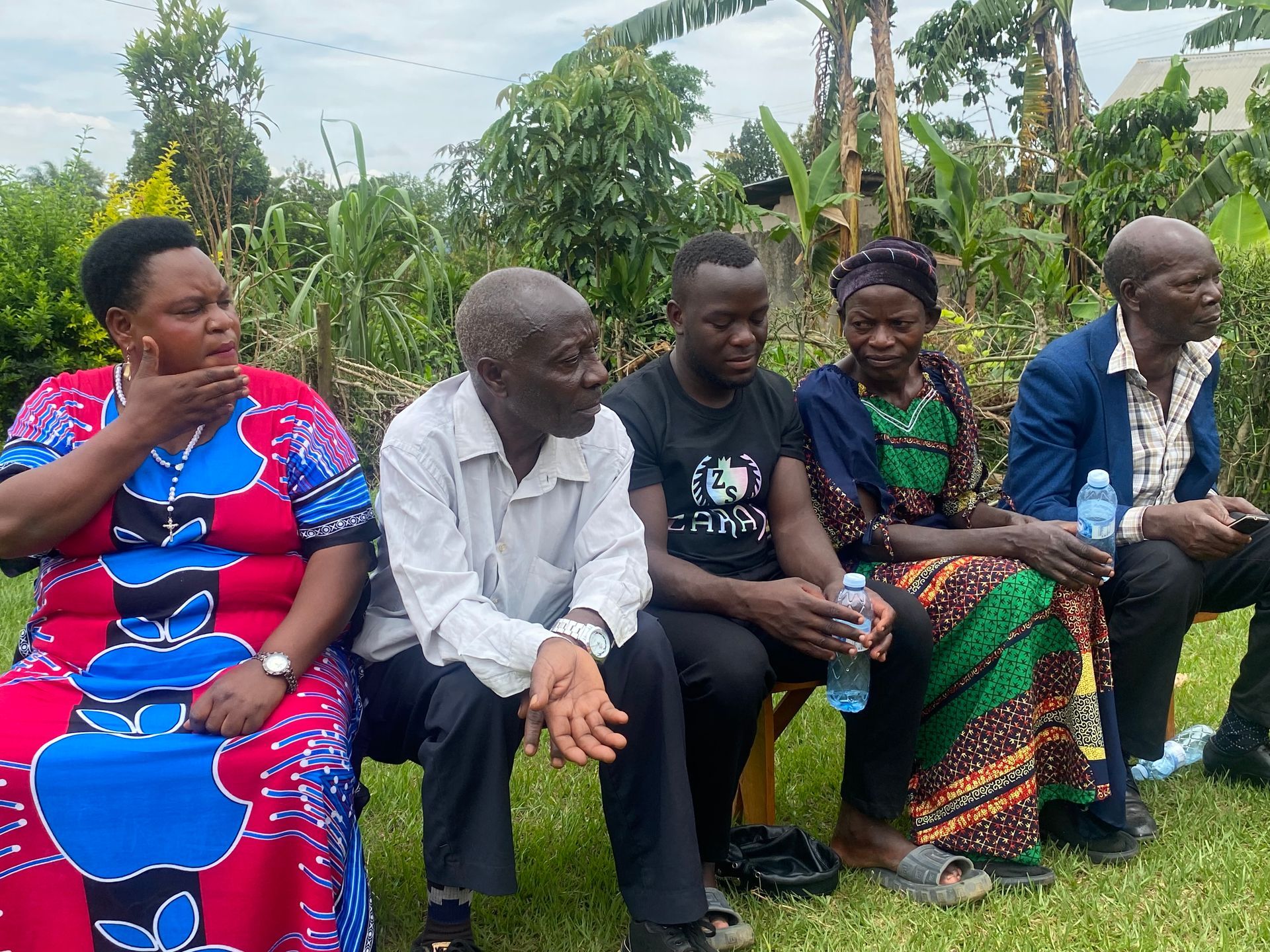
At the Laudara Foundation, we believe that sustainable community development begins at the grassroots level. Our mission is to empower local communities in rural Uganda. To identify and develop impactful community projects it is for us essential to involve the local people, and specifically the village leaders. This collaborative approach not only fosters ownership but also ensures that initiatives are tailored to meet the unique needs of each village.
Governance Structure
Uganda's governance framework is rooted in the Local Government Act of 1997, which established local governments responsible for administrative functions and service delivery in rural areas. This decentralized approach is intended to empower local communities by involving them in decision-making processes and ensuring that resources are allocated according to local needs. This structure is supported by various policies and programs aimed at improving the living conditions of rural populations, which constitute over 75% of the country's population.
Village council
Village councils, known as Local Council I (LCI), are the foundational governance structures that facilitate local administration and community engagement. These councils are composed of elected members who play various roles to ensure effective governance and development at the village level and enhance local participation in decision-making and development processes. A local council ofter exists out some of the following key positions: Chairman, Vice Chair, Secretary, Treasurer and secretaries of different committees like for youth, the elderly, education, security, women’s interest and disabilities
Roles and Responsibilities of Village Leaders
- Community Representation: Village leaders serve as representatives of their communities, voicing the needs and concerns of residents to higher levels of government. They are expected to ensure that all community members, including marginalized groups, have a voice in local governance1.
- Implementation of Development Projects: They are instrumental in implementing community development projects. Their leadership is essential for mobilizing resources, coordinating activities, and ensuring that projects align with community needs.
- Conflict Resolution: Village leaders often act as mediators in disputes within the community, helping to maintain peace and harmony. Their knowledge of local customs and relationships enables them to address conflicts effectively.
- Facilitating Participation: They are tasked with promoting inclusive participation in community affairs. This includes encouraging the involvement of women, youth, and other marginalized groups in decision-making processes
Economic Activities
The majority of rural households depend on agriculture for their livelihoods, with about 89% engaged in farming activities. However, challenges such as climate change, limited market access, and inadequate financial services hinder agricultural productivity. The Ugandan government has initiated various programs to support small businesses, including the provision of loans aimed at helping villagers start or expand their enterprises. One example is the micro loan of unto UGX 1,000,000 that is provided by ASA.
ASA Uganda Ltd, also known as ASA Microfinance Uganda, is a for-profit, non-depository microfinance institution operating in Uganda. It was established in 2013 and is regulated by the Uganda Microfinance Regulatory Authority (UMRA). ASA Uganda is a subsidiary of ASA International, one of the world's largest international microfinance organizations.